Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has garnered significant attention for its potential as a store of value and investment asset. However, like any asset, it comes with its own set of risks, particularly regarding storage. Let's delve into the various risks associated with storing Bitcoin and explore strategies to mitigate them.
Storing Bitcoin online or in digital wallets exposes it to cybersecurity threats such as hacking, phishing, malware, and ransomware attacks. These threats can result in the loss of funds if proper security measures are not in place.
Holding Bitcoin on cryptocurrency exchanges exposes it to the risk of exchange failures, insolvency, or security breaches. Mt. Gox's collapse in 2014 serves as a stark reminder of the risks associated with trusting thirdparty exchanges.
Private keys are essential for accessing and transacting Bitcoin. Losing or compromising these keys can result in the permanent loss of funds. This risk is particularly significant for those who store Bitcoin in noncustodial wallets.
Regulatory uncertainty and changes in legislation can impact the legality and usability of Bitcoin in certain jurisdictions. This uncertainty can affect the value of Bitcoin and the ability to transact with it freely.
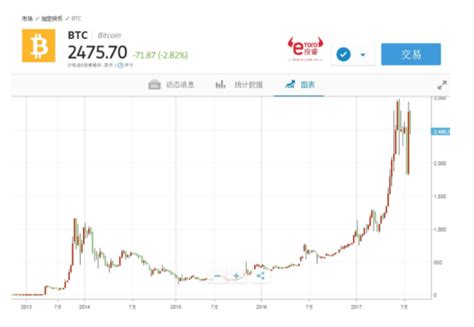
Bitcoin's price volatility exposes holders to market risks. Rapid price fluctuations can result in significant gains or losses depending on the timing of transactions or conversions to fiat currency.
1.
Cold storage involves keeping Bitcoin offline, away from internetconnected devices, thereby reducing exposure to cyber threats. Hardware wallets and paper wallets are popular cold storage solutions.
2.
Multisig wallets require multiple signatures to authorize transactions, adding an extra layer of security against unauthorized access or key compromise.
3.
Diversifying storage across multiple wallets and exchanges can mitigate the risk of a single point of failure. It spreads risk and reduces dependency on any single platform.
4.
Regularly backing up private keys or wallet seeds ensures that funds can be recovered in the event of loss or damage to hardware wallets or storage devices.
5.
Practicing good cybersecurity hygiene, such as using strong, unique passwords, enabling twofactor authentication, and keeping software up to date, helps mitigate the risk of hacking and malware attacks.
6.
Adhering to regulatory requirements and staying informed about changes in legislation can help mitigate regulatory risks associated with Bitcoin storage and usage.
Understanding and mitigating the risks associated with Bitcoin storage are crucial for safeguarding your investment. By employing a combination of security best practices and diversification strategies, investors can minimize the likelihood of loss due to cyber threats, exchange failures, or regulatory changes, thus enabling them to confidently hold and transact with Bitcoin.
版权声明:本文为 “联成科技技术有限公司” 原创文章,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明;

